Time series charts are a powerful tool used in data analysis to visualize trends and patterns over a specific period of time. These charts are widely used in various industries such as finance, economics, and marketing to track and forecast data. A time series chart typically consists of a horizontal axis representing time and a vertical axis representing the data points being measured. By plotting data points at regular intervals, analysts can easily identify patterns, trends, and anomalies.
One of the key benefits of time series charts is their ability to provide insights into historical data trends, making them essential for predicting future outcomes. Time series charts can help analysts identify seasonality, trends, cyclical patterns, and outliers in the data, enabling them to make informed decisions based on past performance.
Types of Time Series Charts
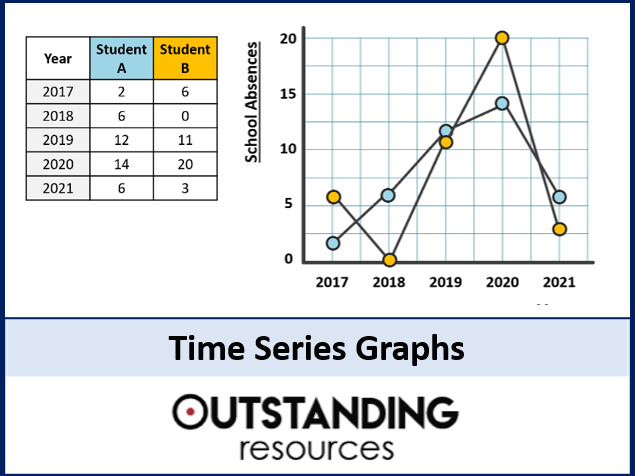
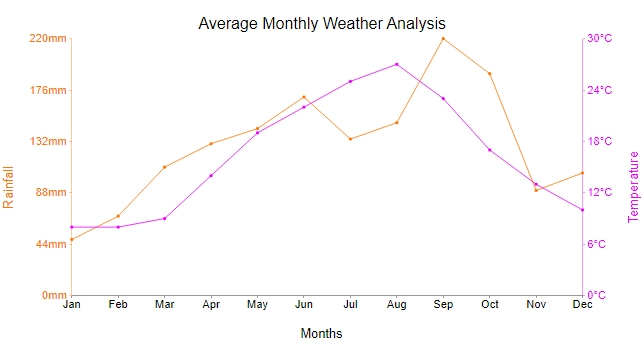
There are several types of time series charts that analysts can use to visualize data effectively. The most common types include line charts, bar charts, area charts, and candlestick charts. Line charts are ideal for showing trends over time, while bar charts are useful for comparing data points at different time intervals. Area charts are great for illustrating cumulative data trends, and candlestick charts are commonly used in financial analysis to track stock prices.
When selecting a type of time series chart, analysts should consider the nature of the data being analyzed and the specific insights they want to gain. By choosing the right type of chart, analysts can effectively communicate their findings and make data-driven decisions that drive business success.
Best Practices for Creating Time Series Charts
When creating time series charts, it’s important to follow best practices to ensure accuracy and clarity in data visualization. One key practice is to choose the appropriate time interval for data points based on the frequency of data collection. For example, daily data points may require a different time interval than monthly or yearly data points.
Additionally, analysts should label axes clearly, provide legends for multiple data series, and use color coding effectively to distinguish between different data sets. It’s also important to ensure that the chart is visually appealing and easy to interpret by avoiding clutter and unnecessary elements that can distract from the main message.
By following these best practices and selecting the right type of time series chart for the data at hand, analysts can unlock valuable insights and make informed decisions that drive business growth and success.