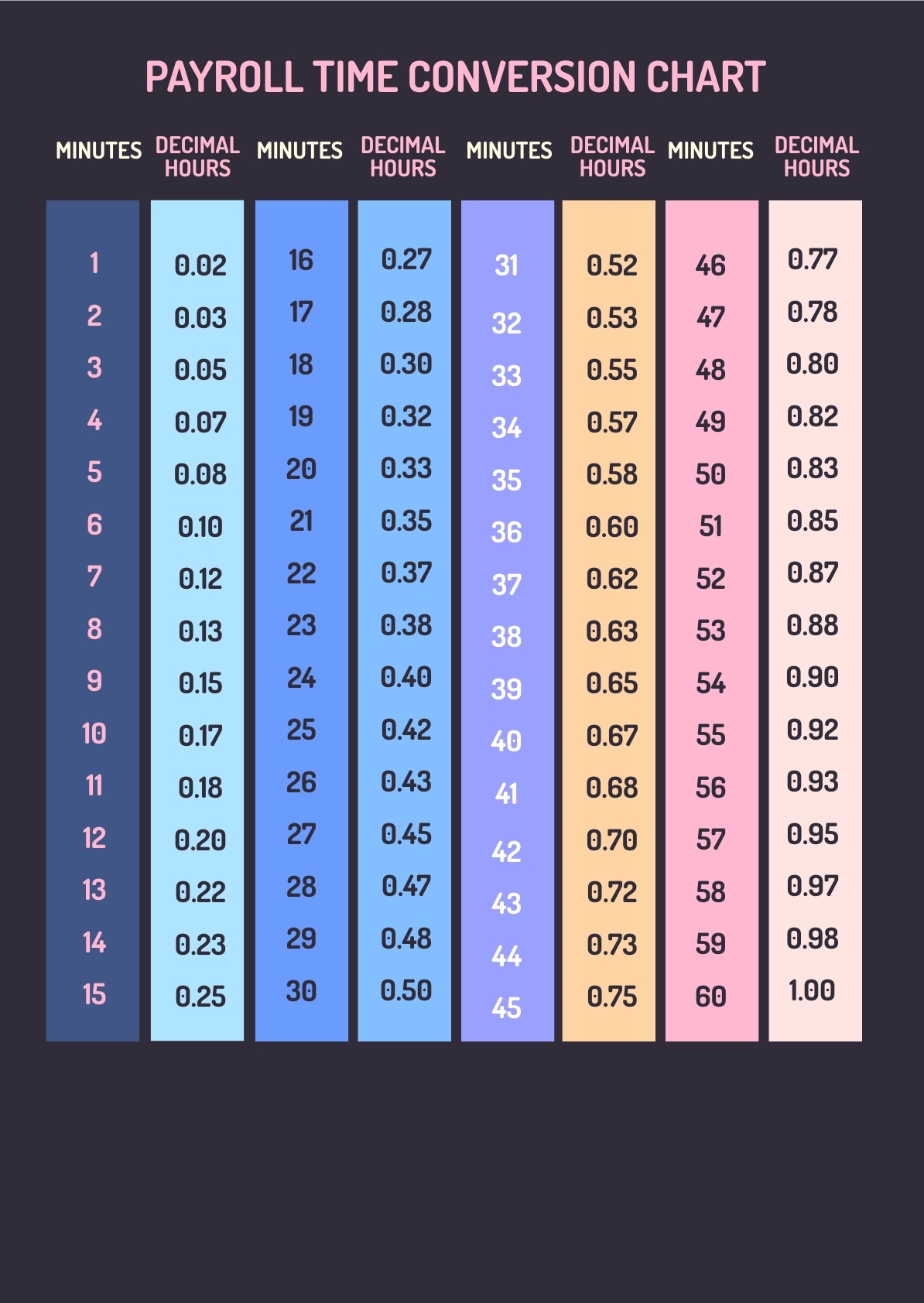
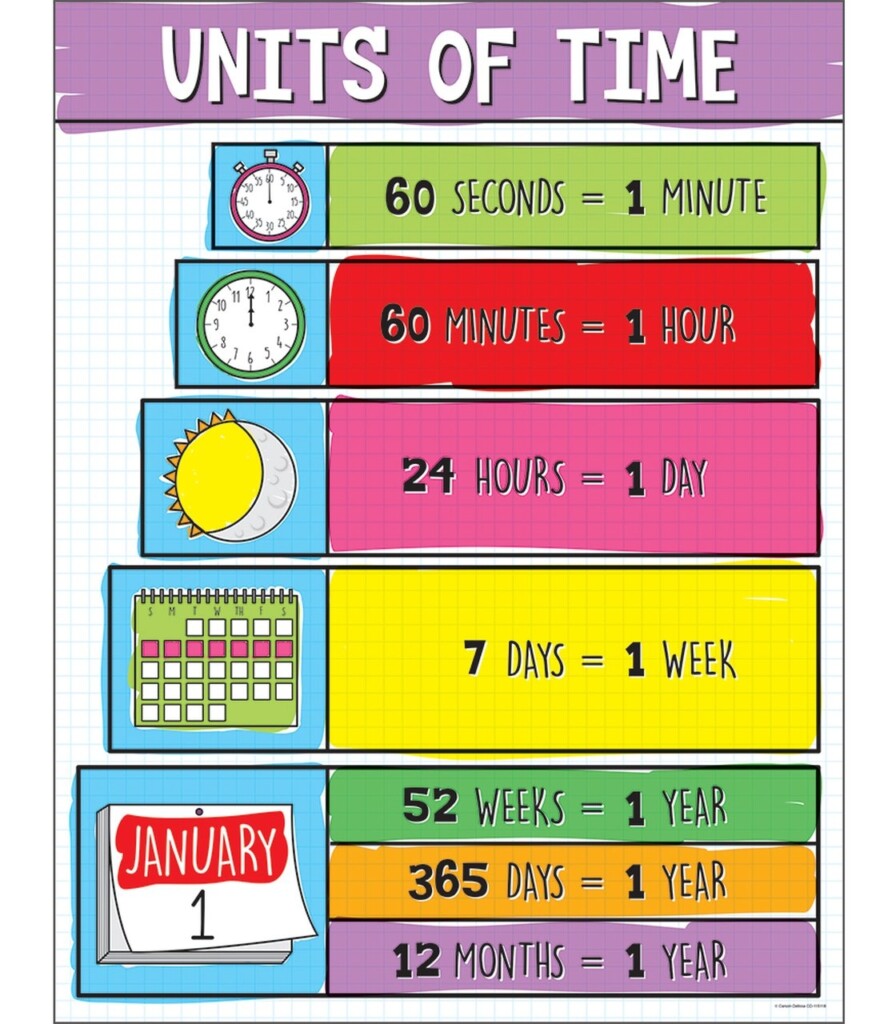
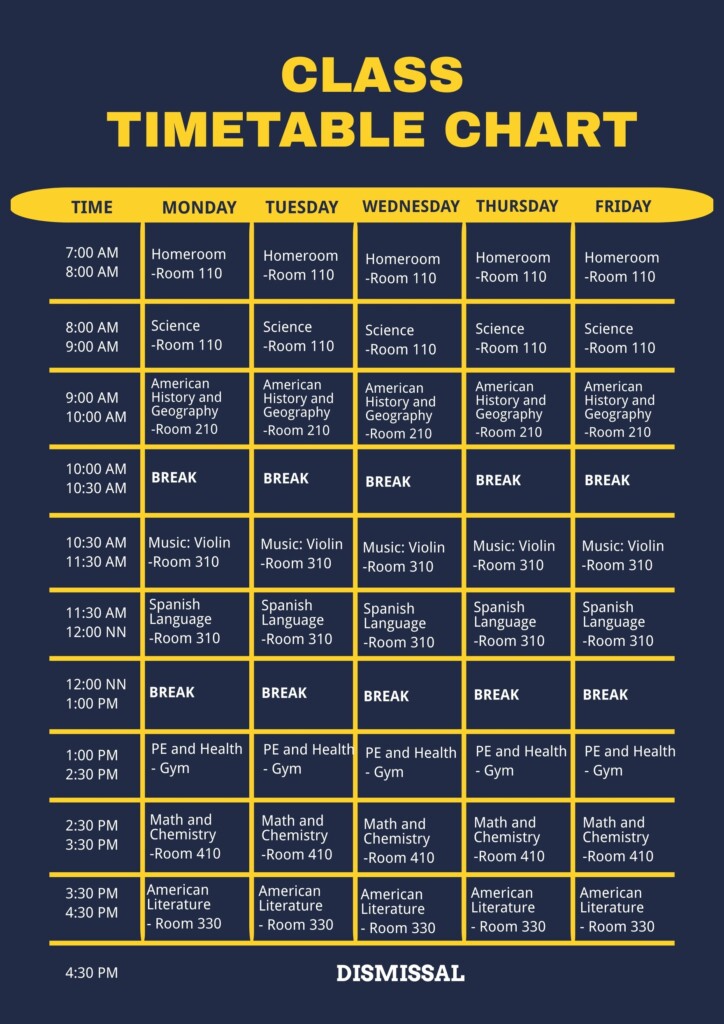
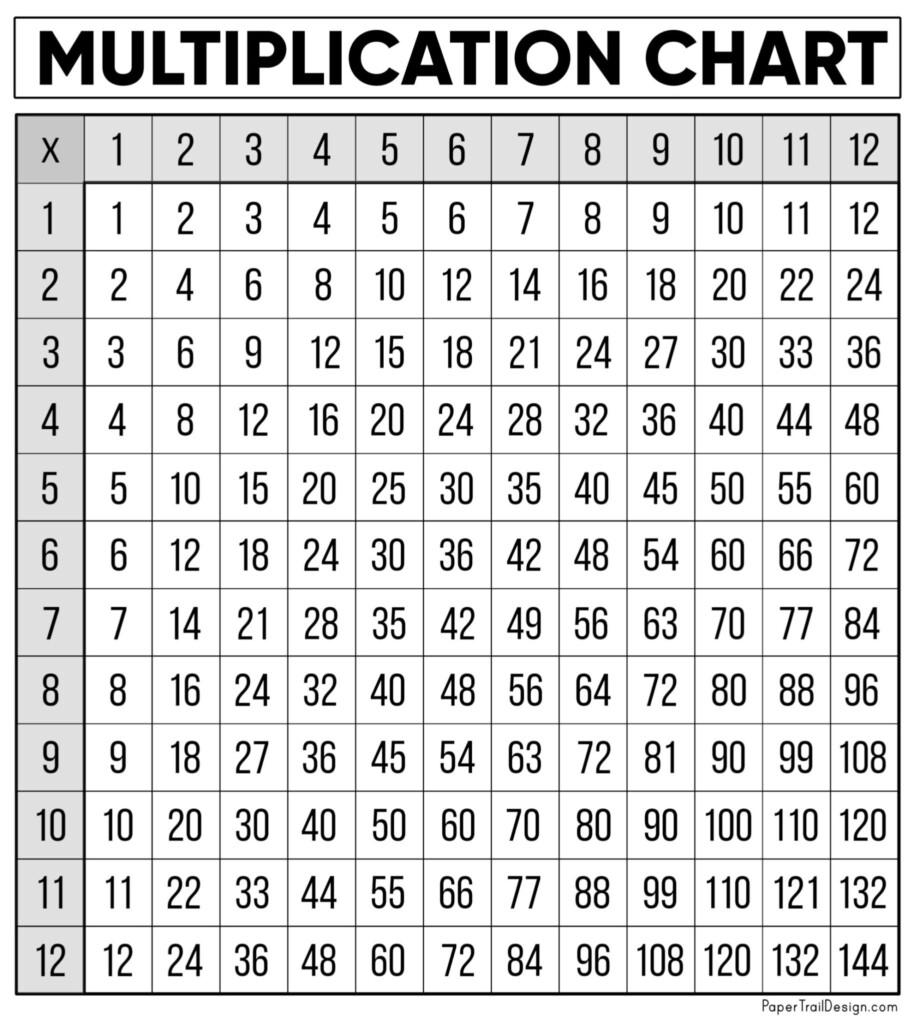
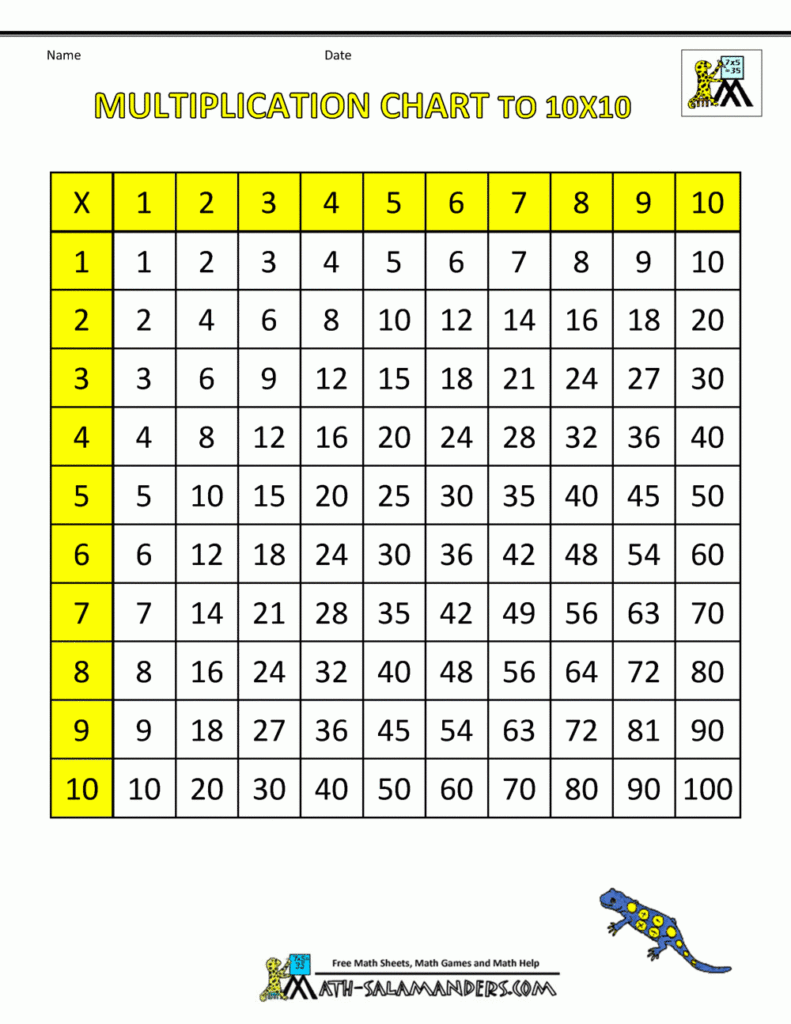
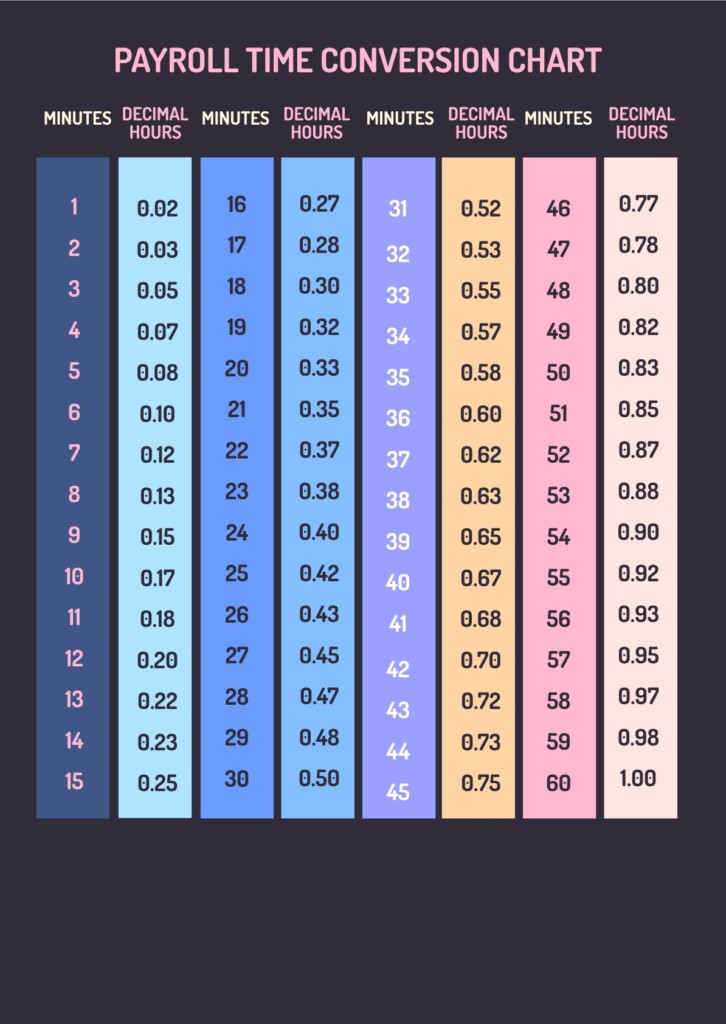
Time charts are essential tools used in various industries to visually represent data over time. Whether tracking project milestones, monitoring sales performance, or analyzing trends, time charts provide a clear and concise way to understand complex information. By organizing data into a chronological sequence, time charts help stakeholders make informed decisions and identify patterns that may not be apparent in a traditional spreadsheet or report.
There are several types of time charts that serve different purposes depending on the data being presented. Line charts are commonly used to show trends and patterns over a continuous time period, while bar charts are effective for comparing data at specific points in time. Gantt charts, on the other hand, are ideal for visualizing project schedules and dependencies. By selecting the appropriate type of time chart, businesses can effectively communicate their data and insights to key stakeholders.
Best Practices for Creating Time Charts
When creating time charts, it is important to follow best practices to ensure clarity and accuracy. Start by selecting the right type of chart that best represents the data you want to convey. Use consistent labeling and formatting to make it easy for viewers to interpret the information. Avoid cluttering the chart with unnecessary elements and focus on highlighting the key insights. Lastly, provide context and explain any trends or anomalies that may be present in the data to help viewers understand the story behind the numbers.
In conclusion, time charts are powerful tools that can help businesses make informed decisions and drive success. By using the right type of chart and following best practices, organizations can effectively communicate their data and insights to stakeholders. Whether tracking progress or analyzing trends, time charts provide a visual representation of data that is both engaging and informative.