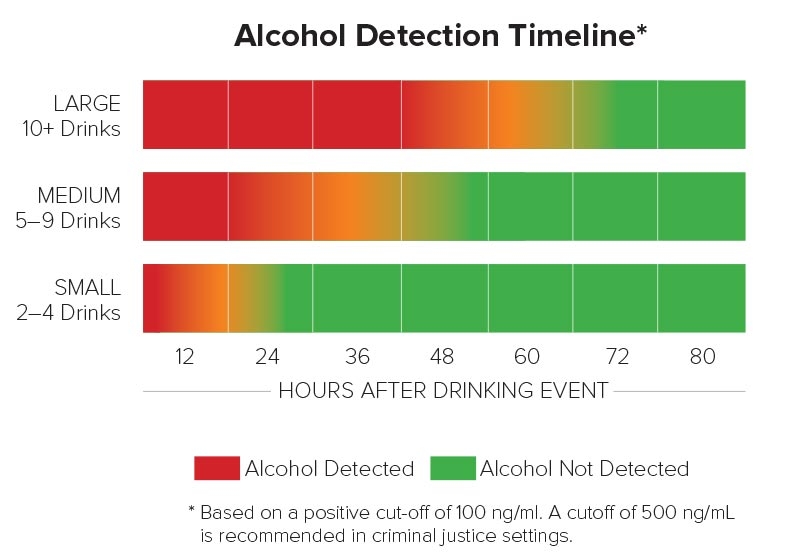
ETG, or Ethyl Glucuronide, is a metabolite of alcohol that can be detected in urine, blood, and hair samples. It is a reliable marker for recent alcohol consumption, as it can be detected in the body for up to 80 hours after drinking. ETG testing is often used in various settings, including probation monitoring, workplace drug testing, and treatment programs.
The ETG detection time chart provides an estimate of how long ETG can be detected in different types of samples after alcohol consumption. While individual factors such as metabolism, hydration level, and amount of alcohol consumed can affect detection times, the following are general guidelines:
Urine: ETG can be detected in urine for up to 3-5 days after alcohol consumption.
Blood: ETG can be detected in blood for up to 24 hours after alcohol consumption.
Hair: ETG can be detected in hair for up to 90 days after alcohol consumption.
Factors Affecting ETG Detection Time
It is important to note that the detection time of ETG can vary based on several factors. These include the frequency of alcohol consumption, the amount of alcohol consumed, the type of alcohol consumed, metabolism rate, and hydration level. Additionally, some medications and health conditions can also affect the detection of ETG in the body.
Overall, the ETG detection time chart can provide a general idea of how long ETG can be detected in different samples after alcohol consumption. However, it is always best to consult with a healthcare professional or testing provider for accurate and personalized information regarding ETG detection times.